The Glymphatic System
- brain-wide waste clearance
The brain has a tight blood-brain barrier limiting the re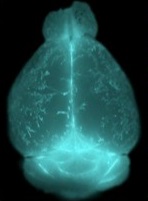 moval of solutes to the vascular compartment, and does not contain any lymphatic vessels. Instead, a peri-vascular bulk flow system, named the glia-lymphatic (glymphatic) system, facilitates brain-wide clearance. The glymphatic system mediates exchange of solutes and peptides, such as amyloid beta, between the brain parenchyma and the cerebrospinal fluid. The system received its name due to the crucial role of astrocytes’ aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channels for this system. Due to this clearance function, it is believed that the glymphatic system and astrocytes are crucial for removing metabolites and thus maintaining a healthy milieu and preventing diseases.
moval of solutes to the vascular compartment, and does not contain any lymphatic vessels. Instead, a peri-vascular bulk flow system, named the glia-lymphatic (glymphatic) system, facilitates brain-wide clearance. The glymphatic system mediates exchange of solutes and peptides, such as amyloid beta, between the brain parenchyma and the cerebrospinal fluid. The system received its name due to the crucial role of astrocytes’ aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channels for this system. Due to this clearance function, it is believed that the glymphatic system and astrocytes are crucial for removing metabolites and thus maintaining a healthy milieu and preventing diseases.
Latest articles
Astrocytes
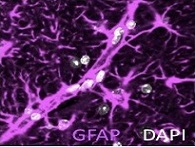 Astrocytes are the key regulators of brain homeostasis. Their endfeet processes ensheath the cerebral vasculature and contact thousands of synapses. We are interested in the endfeet of astrocytes, as they form perivascular pathways used by the glymphatic system for fluid transport. Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channels in the astrocyte endfeet are crucial for influx of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the brain and clearance of solutes. Besides AQP4 molecular drivers of glymphatic flow remain elusive.
Astrocytes are the key regulators of brain homeostasis. Their endfeet processes ensheath the cerebral vasculature and contact thousands of synapses. We are interested in the endfeet of astrocytes, as they form perivascular pathways used by the glymphatic system for fluid transport. Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) water channels in the astrocyte endfeet are crucial for influx of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into the brain and clearance of solutes. Besides AQP4 molecular drivers of glymphatic flow remain elusive.
Neuroimmunology
Similar to the lymphatic system, the glymphatic system connects to lymph nodes in the cervical region. Thus, there is a strong association between glymphatic and immune function. Fluid drains from the brain into meningeal lymphatic vessels, to the nasal mucosa via the cribriform plate, via spinal and cranial nerves, or simply perivenously. Drainage from the brain will mount an immune response in cervical lymph nodes. The idea of the brain being ‘immune privileged’ remains true in the sense that there are much fewer patrolling T cells in the brain e.g. than in the skin. However, meningeal lymphatic vessels and CSF efflux to cervical lymph via the nasal mucosa is understudied in relation to central nervous system immune function.

